Coinbase Highlights Lightning Network’s Potential Disruption of the $150,000,000,000 Payments Industry

Crypto exchange Coinbase says that the Lightning Network has the potential to disrupt the massive $150 billion payments industry.
Lightning Network is a layer-2 scaling solution built on top of Bitcoin that aims to enable instant and cost-effective transactions for BTC.
In a new blog post, Coinbase says the Lightning Network is targeting a more real-world use case compared to much of the speculative-driven growth on smart contract platforms.
With Visa and Mastercard pulling in around $24 billion in 2021 by collecting 2-3% of every transaction completed with their cards, Coinbase says the Lightning Network could be the innovation that undercuts the world’s largest payment processors.
“Humble beginnings aside, the potential to turn crypto’s most valuable asset into a true medium of exchange has the power to bring greater financial inclusion to anyone with a smartphone. The ability to cost-effectively route fiat transactions over Lightning rails without users ever knowing they’re using Bitcoin can disrupt $150B+* a year industries.
What Visa/Mastercard is for fiat currencies, Lightning can be for Bitcoin. The combination of a universally accessible payment network atop the world’s first open-source protocol for money can help Bitcoin evolve into a true global reserve currency.”
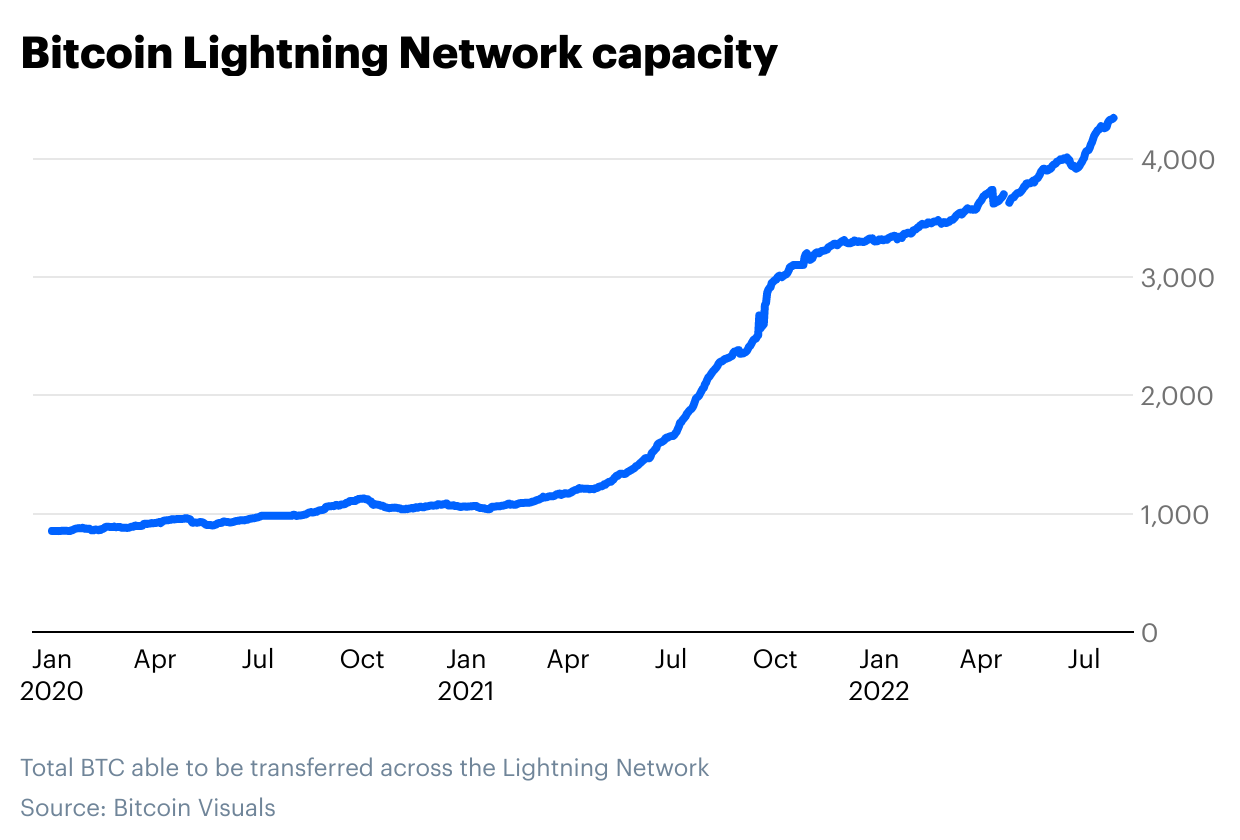
Source: Coinbase
While Lightning has much potential, Coinbase notes that adoption is still slow. In addition, Lightning has to overcome the massive network effects of Visa and Mastercard.
“Lightning is still cumbersome for new users and merchants. Additionally, onboarding low-income users in developing countries remains a major challenge to fulfilling the promise of Lightning remittances.
Lastly, the lack of compliance and regulatory frameworks limit the ability for existing payment and banking service providers to onboard and serve a global customer base.”
Coinbase says that should Lightning Network become meaningfully adopted, we can expect developing countries with high inflation and “more smartphones than bank accounts” to lead the way.






 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Cardano
Cardano  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Chainlink
Chainlink  LEO Token
LEO Token  Zcash
Zcash  Monero
Monero  Stellar
Stellar  Litecoin
Litecoin  Hedera
Hedera  Dai
Dai  Cronos
Cronos  OKB
OKB  Tether Gold
Tether Gold  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic  KuCoin
KuCoin  Gate
Gate  Algorand
Algorand  Cosmos Hub
Cosmos Hub  VeChain
VeChain  Tezos
Tezos  Dash
Dash  Stacks
Stacks  TrueUSD
TrueUSD  IOTA
IOTA  Basic Attention
Basic Attention  Decred
Decred  Theta Network
Theta Network  NEO
NEO  Synthetix
Synthetix  Qtum
Qtum  Ravencoin
Ravencoin  0x Protocol
0x Protocol  DigiByte
DigiByte  Zilliqa
Zilliqa  Nano
Nano  Holo
Holo  Siacoin
Siacoin  Numeraire
Numeraire  Waves
Waves  Ontology
Ontology  Enjin Coin
Enjin Coin  Status
Status  BUSD
BUSD  Hive
Hive  Pax Dollar
Pax Dollar  Lisk
Lisk  Steem
Steem  Huobi
Huobi  OMG Network
OMG Network  NEM
NEM  Bitcoin Gold
Bitcoin Gold  Augur
Augur  Ren
Ren