EIP 4337 Activated by Ethereum (ETH): Comprehensive Guide

With the new function activated, every owner of a noncustodial Ethereum (ETH) wallet can dramatically increase its functionality and make his/her experience with Ethereum (ETH) and EVM-compatible blockchains secure.
EIP 4337 goes live on Ethereum (ETH): Highlights
Yesterday, on March 1, 2023, Ethereum (ETH) developers announced that the Account Abstraction mechanism included in Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP 4337) was stress tested, audited and deployed to mainnet.
- Being in discussions since 2016, Account Abstraction is among the most ambitious changes of Ethereum’s (ETH) design;
- EIP 4337 is co-developed by the Ethereum Foundation and a number of heavy-hitting Web3 teams: Stackup, Biconomy, Alchemy; OpenZeppelin performed its security audit;
- It blurs the line between Externally Owned Accounts (wallets) and Contract Accounts (smart contracts) and introduces a new instrument in Ethereum: Smart Accounts;
- This update is of paramount importance for the security, operability and massive adoption of the Ethereum (ETH) blockchain;
- Besides Ethereum (ETH), this update goes live on all EVM-compatible blockchains: Polygon Network (MATIC), BNB Chain (BSC), Ethereum’s L2 networks and so on.
With EIP 4337 activated, Ethereum (ETH) users can turn their noncustodial wallets into full-stack decentralized banks. This protects new users from losing access to their ETH wallets due to seed phrase issues.
What is EIP?
Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) are descriptions for standards on the Ethereum (ETH) network: core protocol specifications, client APIs and contract standards. Major network upgrades are associated with the mainnet implementation of this or that EIP.
Ethereum (ETH) enthusiasts submit their proposals for discussion and review; the full cycle of approval takes eight phases. Some sophisticated EIPs caused heated debates and were discussed for years.
EIP 20 (introduction of ERC-20 tokens on Ethereum), EIP 721 (non-fungible token standard), and EIP 1559 (dynamic transactional fee model with periodic token burn events) are among the most crucial EIPs since Ethereum’s (ETH) inception.
What are EOAs and CAs on Ethereum?
Ethereum, a first-ever blockchain network with smart contracts support (programmable blockchain), has two types of accounts in its design. Simply put, not unlike traditional banking and payment apps, an Ethereum (ETH) account is where cryptocurrency is stored.
Externally Owned Accounts (or EOAs) can store cryptocurrency but are not able to send transactions themselves. Users need to authorize the transactions with private keys. Crypto wallets like MetaMask are textbook examples of EOAs.
By contrast, Contract Accounts are software programs that can perform financial operations. They are controlled by code, not private keys. Smart contracts — basic elements of DeFi and NFT protocols — are «Contract Accounts» (CAs) by design.
What is EIP 4337 or Account Abstraction (AA)?
EIP 4337 is an upgrade of the Ethereum (ETH) network’s design; it is implemented as an additional layer on the top of the Ethereum (ETH) mainnet, so it did not need a hard fork to go live. With Account Abstraction, Ethereum (ETH) users can easily turn their wallet into a smart contract and supercharge them with extra functionality.
A «smart account» is a new type of wallet that becomes available with EIP 4337. First and foremost, average users will be able to turn their accounts into multi-signature storage. This will eliminate the need for account owners to be responsible for private keys.
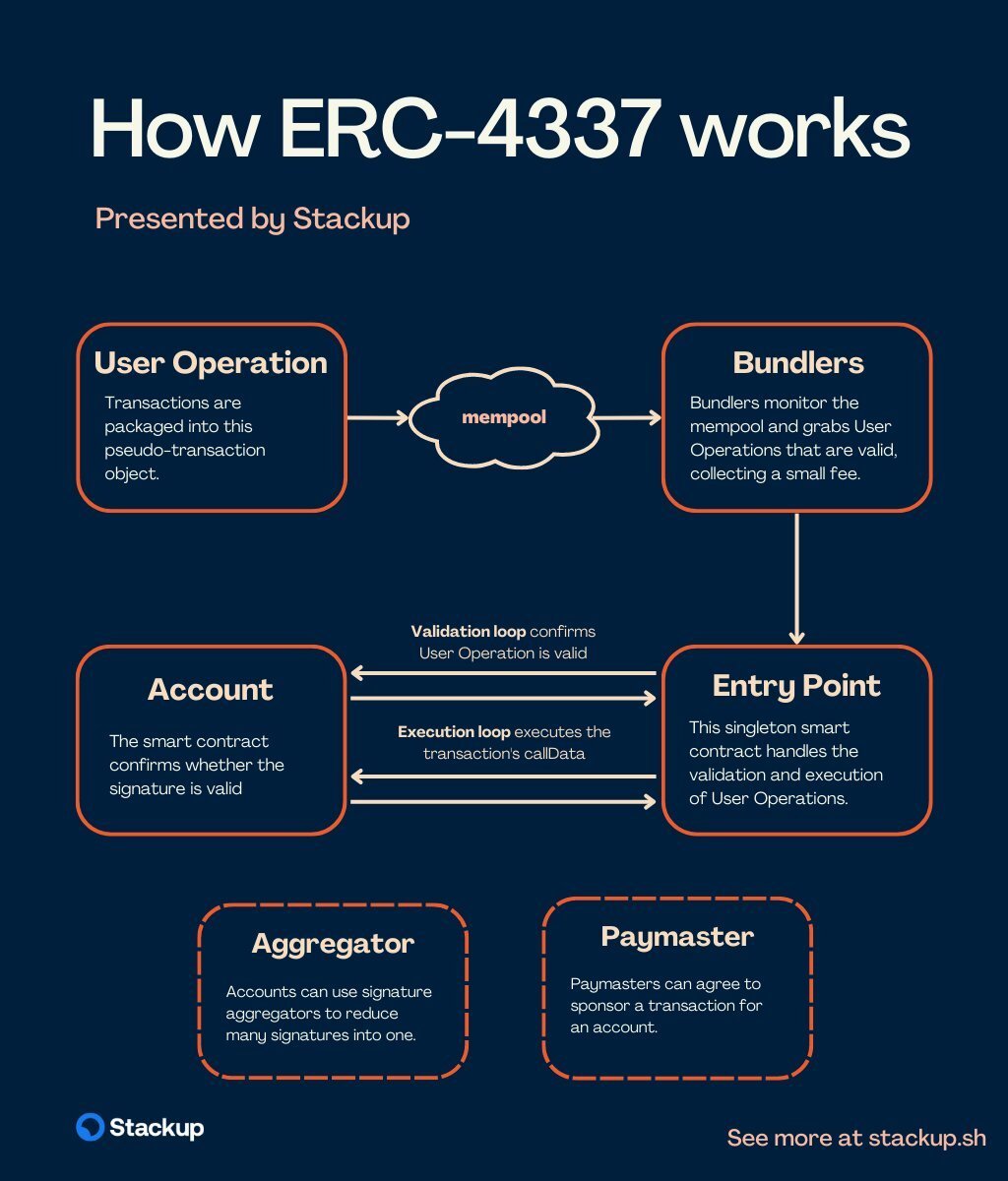
The Ethereum Foundation highlights that EIP 4337 will allow the use of the results of off-chain computations on-chain, which is truly game changing for making Ethereum (ETH) feature-rich:
ERC-4337 attempts to do the same thing that EIP-2938 does, but through extra-protocol means. Users are expected to send off-chain messages called user operations, which get collected and packaged in bulk into a single transaction by either the block proposer or a builder producing bundles for block proposers. The proposer or builder is responsible for filtering the operations to ensure that they only accept operations that pay fees. There is a separate mempool for user operations, and nodes connected to this mempool do ERC-4337-specific validations to ensure that a user operation is guaranteed to pay fees before forwarding it.
Since the first days of EIP 4337 operations — as revealed by John Rising, Stackup co-founder and vocal upgrade proponent — the new functionality has a solid infrastructure background and is available on all major EVM-compatible blockchains.
How EIP 4337 will change Ethereum (ETH) forever
EIP 4337 has already made it into the top ranking of the most important and ambitious EIPs in Ethereum’s (ETH) history. With EIP 4337 activated, the Ethereum (ETH) experience for a new generation of users and developers will be different.
EIP 4337 for security
When it comes to private key management, EIP 4337 makes it possible for various users to authorize transactions from one account. As such, Ethereum (ETH) holders can integrate their wallet with a smartphone to streamline key management and add an extra recovery instrument for their coins.
EIP 4337 for usability
When it comes to smart contracts, EIP 4337 paves the way for 100% «gas-less» contracts: now developers can hard-code the opportunity to utilize this or that wallet as a source for gas payments. Previously, such a design needed all transactions to be authorized with private keys.
EIP 4337 for massive adoption
All enthusiasts, proponents and developers of EIP 4337 are certain that it will make the user experience of Ethereum (ETH) more newbie friendly. The Ethereum (ETH) toolkit becomes more feature-rich than ever before. Now it enables more sophisticated and eccentric designs that would have been impossible without «smart accounts.»
Wrapping up: What’s next for Account Abstraction in EVM?
As such, EIP 4337 activation is a major milestone for Ethereum (ETH) in 2023. While it now appears overshadowed by the hotly-anticipated Shanghai upgrade (and its economic promises), Account Abstraction is as important for Ethereum’s (ETH) tooling as EIP 721 and EIP 1155.
Meanwhile, this story is far from over: in Vitalik Buterin’s roadmap are long-term goals for Account Abstraction. Mandatory conversion to EIP 4337-compatible accounts and censorship-resistant practices would be the next steps in AA development for Ethereum.






 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Cardano
Cardano  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Chainlink
Chainlink  Monero
Monero  LEO Token
LEO Token  Stellar
Stellar  Zcash
Zcash  Litecoin
Litecoin  Hedera
Hedera  Dai
Dai  Cronos
Cronos  Tether Gold
Tether Gold  OKB
OKB  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic  KuCoin
KuCoin  Cosmos Hub
Cosmos Hub  Gate
Gate  Algorand
Algorand  VeChain
VeChain  Stacks
Stacks  Tezos
Tezos  TrueUSD
TrueUSD  Dash
Dash  IOTA
IOTA  Basic Attention
Basic Attention  Theta Network
Theta Network  Decred
Decred  NEO
NEO  Synthetix
Synthetix  Qtum
Qtum  Ravencoin
Ravencoin  0x Protocol
0x Protocol  DigiByte
DigiByte  Zilliqa
Zilliqa  Nano
Nano  Siacoin
Siacoin  Holo
Holo  Numeraire
Numeraire  Waves
Waves  Status
Status  Ontology
Ontology  Enjin Coin
Enjin Coin  BUSD
BUSD  Hive
Hive  Pax Dollar
Pax Dollar  Lisk
Lisk  Steem
Steem  Huobi
Huobi  OMG Network
OMG Network  Bitcoin Gold
Bitcoin Gold  NEM
NEM  Bitcoin Diamond
Bitcoin Diamond  Augur
Augur