Has Proof of Stake Made Ethereum More Centralized?
As Ethereum continues on its journey towards a more sustainable and decentralized future, it faces a conundrum: has the shift to Proof of Stake made the network more centralized?
Here we delve into the intricacies of the centralization debate, examining the various benefits and challenges of PoS, and exploring the potential impact of Ethereum’s ongoing upgrades on its commitment to decentralization.
A Green Revolution: PoS and Environmental Impact
Ethereum’s transformation to Proof of Stake (PoS) purports to pave the way for a sustainable future. Unlike the energy-intensive Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism, PoS dramatically reduces Ethereum’s carbon footprint. Bitcoin, for instance, has faced backlash for its massive energy consumption. As Ethereum champions a more eco-friendly alternative, it joins the global fight against climate change and aims to set a precedent for other blockchain networks.
The Rise of the Little Guy: PoS and Inclusivity
In PoW systems, miners with powerful hardware and abundant resources dominate the network. Smaller participants struggle to compete against these well-equipped giants. PoS, however, enables users with lesser amounts of ETH to partake in the network.
By fostering a more inclusive environment, Ethereum promotes decentralization and network resilience. The shift to PoS resonates with the blockchain community’s vision for a more egalitarian network, where participants of various sizes can contribute.
Validators secure the network in PoS systems by putting their stakes at risk. Misbehaving or failing to validate transactions may result in a loss of stake. This penalty fosters a strong incentive for validators to act in the network’s best interest. As a result, Ethereum’s security receives a boost. A secure network attracts more users and developers, driving growth and confidence in the ecosystem.
The Dark Side: Centralization Concerns in PoS
Despite its appeal, PoS raises the issue of centralization. Validators with considerable stakes possess broad influence over the network. These large stakeholders may dominate transaction validation, leading to a consolidation of power. This concentration flies in the face of Ethereum’s core principle of decentralization.
One example of centralization is the potential for cartels or collusion among large stakeholders. Validators may band together to manipulate the network, leading to bad outcomes. Ethereum must confront these issues to preserve its decentralized nature.
A High-Stakes Game: Entry Barriers
To participate in PoS validation, users must meet a minimum ETH stake requirement. While this barrier helps maintain network security, it could deter smaller players from entering the fray. As larger stakeholders gain prominence, centralization fears intensify. To ensure a truly decentralized network, Ethereum must balance stake requirements with broad participation.
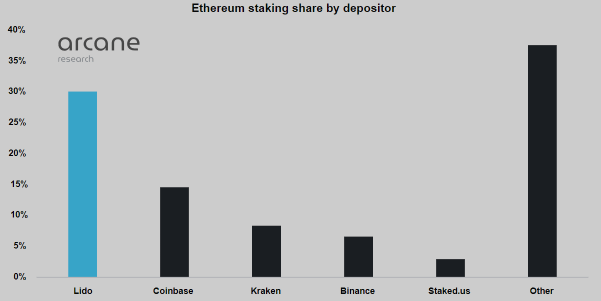
The Merge has shed light on potential ETH centralization concerns. Source: Dune Analytics
Risky Business: The Perils of Staking
Staking in PoS systems introduces new risks. Validators may lose their stakes due to software bugs, security breaches, or user errors. While risks are inherent in any system, PoS amplifies the stakes. Validators must proceed with caution, aware of the lurking dangers.
Furthermore, the introduction of slashing in Ethereum’s PoS system penalizes validators for not following protocol rules. Although slashing enhances security, it also increases the complexity and potential pitfalls for validators. Consequently, staking becomes a high-risk, high-reward endeavor.
Ethereum’s Evolution: The Merge and the Shanghai Upgrade
Ethereum’s path to PoS involves a series of crucial upgrades, including The Merge and the Shanghai upgrade. These developments comprise milestones in Ethereum’s journey towards realizing the ideal of a more efficient, secure, and decentralized network.
The Merge: Integrating PoW and PoS
The Merge refers to the integration of Ethereum’s current PoW mainnet with the PoS Beacon Chain. This event marks Ethereum’s complete transition to Proof of Stake, effectively merging the two parallel systems into one. The Merge is a critical step in Ethereum’s evolution, as it represents the realization of its long-awaited shift from energy-intensive PoW to the more sustainable PoS.
As Ethereum transitions to PoS, The Merge could potentially influence the centralization debate. The new consensus mechanism brings with it various benefits and challenges that could either promote or undermine decentralization. Observing how The Merge unfolds and its impact on the network’s distribution of power will be crucial in understanding the broader implications of PoS for Ethereum’s centralization.
Shanghai Upgrade: Enhancing Ethereum’s Infrastructure
Initially planned for 2022, the Shanghai upgrade aimed to introduce various improvements and features, such as account abstraction, statelessness, and other enhancements.
However, Ethereum’s core developers decided to prioritize The Merge before the Shanghai upgrade, as the complete transition to PoS is deemed more pressing.
Once the Shanghai upgrade is in full effect, it will play a role in refining Ethereum’s infrastructure, addressing lingering issues, and further optimizing the network. These enhancements could also have implications for the centralization debate, as improved efficiency, security, and accessibility may either encourage greater decentralization or inadvertently lead to centralization tendencies.
The Role of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The DeFi ecosystem, built primarily on Ethereum, has democratized access to financial services. As Ethereum transitions to PoS, DeFi could play a role in the centralization debate. Staking pools and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) may enable smaller stakeholders to pool their resources and take part in the network. These innovations could counterbalance the influence of larger stakeholders and foster decentralization.
Looking Ahead: Ethereum’s Decentralization Dilemma
Ethereum’s transition to PoS has sparked a contentious debate on centralization. The new consensus mechanism offers notable advantages such as environmental sustainability, higher participation, and enhanced security. Yet, it also raises centralization concerns as potential drawbacks emerge, like the dominance of large stakeholders and barriers to entry for smaller participants.
As Ethereum navigates this new terrain, it must address these challenges to preserve its decentralized essence. The blockchain community will need to remain vigilant and work as one to strike a balance between the benefits of PoS and the centralization risks it poses.
Moreover, Ethereum’s developers and community must continue exploring innovative solutions. For instance, enhancing the role of DeFi in staking, refining slashing mechanisms, and fostering a more inclusive environment for all participants can help counter centralization.
Balancing Decentralization and Progress
Ultimately, Ethereum’s success in maintaining decentralization will depend on its ability to adapt and evolve. As the network embraces PoS, it enters a new chapter in its journey, rife with both opportunities and challenges. Ethereum’s future hinges on its capacity to uphold its core values while adapting to the demands of an ever-changing technological landscape.
Ethereum’s shift to Proof of Stake offers undeniable benefits, but the centralization debate continues as potential downsides surface. The Ethereum community must face these challenges head-on to ensure that its decentralized vision perseveres amid new and emerging risks. The ongoing dialogue and collaboration within the community will play a critical role in shaping Ethereum’s future and maintaining its commitment to decentralization.






 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Cardano
Cardano  Monero
Monero  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Chainlink
Chainlink  LEO Token
LEO Token  Stellar
Stellar  Zcash
Zcash  Litecoin
Litecoin  Hedera
Hedera  Dai
Dai  Cronos
Cronos  Tether Gold
Tether Gold  OKB
OKB  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic  KuCoin
KuCoin  Cosmos Hub
Cosmos Hub  Gate
Gate  Algorand
Algorand  VeChain
VeChain  Stacks
Stacks  Dash
Dash  Tezos
Tezos  TrueUSD
TrueUSD  IOTA
IOTA  Decred
Decred  Theta Network
Theta Network  Basic Attention
Basic Attention  NEO
NEO  Synthetix
Synthetix  Qtum
Qtum  0x Protocol
0x Protocol  Ravencoin
Ravencoin  Zilliqa
Zilliqa  DigiByte
DigiByte  Nano
Nano  Holo
Holo  Siacoin
Siacoin  Numeraire
Numeraire  Waves
Waves  Ontology
Ontology  Status
Status  Enjin Coin
Enjin Coin  BUSD
BUSD  Hive
Hive  Pax Dollar
Pax Dollar  Lisk
Lisk  Steem
Steem  Huobi
Huobi  OMG Network
OMG Network  Bitcoin Gold
Bitcoin Gold  NEM
NEM  Augur
Augur